You’ve likely heard the buzz (and indeed the existential questions) surrounding tools like ChatGPT, GPT-4, and other LLMs (large language models). But what exactly are LLMs, and how can you use these AI-tools for SEO and content development? Let’s look closer at this intersection of technology and functionality—and how to put it to good use.
What are LLMs like ChatGPT?
Large language models use probabilities and a massive dataset of information to predict words and phrases that will fit your needs. They have inherent limitations, including the finite nature of their dataset from which they draw information, and should not be used to replace human skills—at least not yet.
Models such as Google’s BERT and LaMDA and OpenAI’s GPT-3 are being used to generate language of all kinds—from code for a website to poetry about the color red—while professionals and educators scramble to identify where these tools will disrupt their workplace—and where they’re useful.
And believe us: LLMs can be very useful. Let’s first define what each term means, and then look at how ChatGPT and its siblings should be used or avoided for today’s SEO tasks.
What is the difference between ChatGPT and GPT-3?
GPT-3 is a Large Language Model created by OpenAI and released in 2020. GPT stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer, meaning it is trained using internet data to generate various types of text and uses a neural network machine learning approach. GPT-3’s deep-learning neural network is built to train the system with over 175 billion machine learning parameters, primarily from content scraped from the web.
ChatGPT, on the other hand, is aimed at enabling interaction in a conversational way. Unlike GPT-3, it is optimized for dialogue, which is why it can answer questions, admit mistakes, challenge false premises provided in the prompt, and reject inappropriate requests. This model has been trained on GPT-3 using reinforcement learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)—a methodology that rewards the tool when it learns from errors and self-adjusts, with the aim to provide the best possible outcome based on human feedback.
LLMs in Machine learning
One of the most popular applications of these models is language generation. Models such as BERT, GPT-3, and LaMDA have defied the machine learning paradigm when it comes to growth, increasing 10x every year for the last few years and setting a precedent for growth beyond traditional projections.
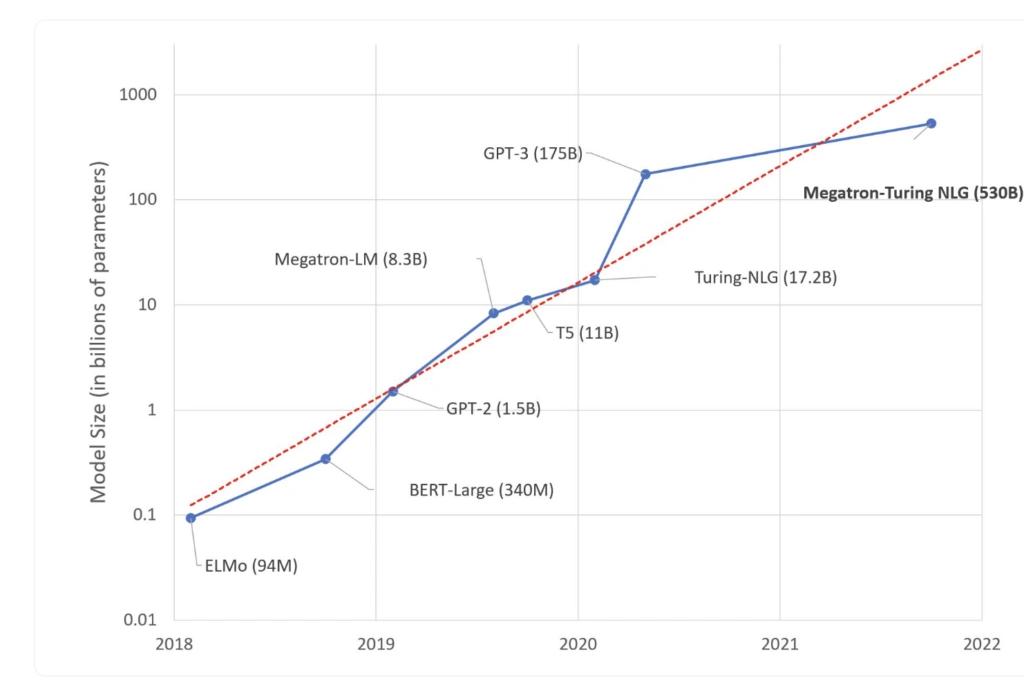
Large Language Models can be defined by these important characteristics:
- LLMs require vast amounts of data to train the machine learning model and for data extraction or processing.
- They utilize neural networks, a subset of deep learning, to process data and identify patterns.
- Maintaining them often has an adverse effect on the environment due to the significant compute resources required to run them consistently.
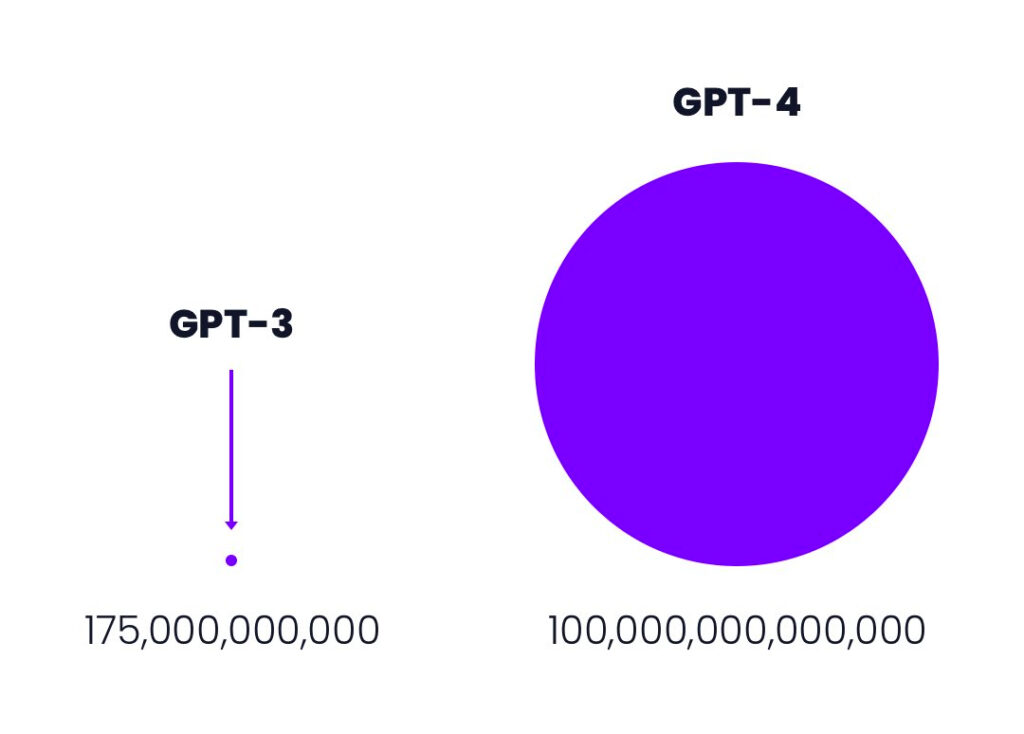
They are trained in large data sets. GPT-4, for instance, is expected to be trained on about 100 trillion parameters (see below).
How to use LLM models in SEO
LLMs can be used to streamline an array of SEO tasks:
- Language generation – Generate titles, meta descriptions, Q&A snippets or answers to frequently asked questions, but always edit these for accuracy, brand tone, and appropriateness for their intended use.
- Structure enhancement – Generate a heading structure based on the existing content on a page.
- Sentiment analysis – Get content labeling for sentiment detection, which is particularly useful when analyzing first-party feedback data or reviews.
- Translation – Translate content roughly to and from other languages.
- Programming and Coding – Get support with the implementation of technical SEO tasks—like code generation for platforms like BigQuery or Looker Studio, support in programming tasks, or generating code snippets for structured data, hreflang implementation, or regex.
However, even with all of these exciting use cases, there are some caveats. After comparing Google Cloud’s APIs to ChatGPT and GPT3, we’ve found that Google Cloud performs much better on most of these tasks in the ways that you’re expecting them to work.
While these models might be able to complete these tasks, they might not always perform as expected, and it’s important to know that there might be better, more tailored APIs to use.
For more on this distinction, view “Machine Learning in Search: Google’s ML APIs vs. OpenAI’s APIs for SEO Use Cases” by Intrepid’s own Lazarina Stoy.
How not to use LLMs in SEO
LLMs can certainly be beneficial, but they still have several limitations. LLMs are not ideal for the following use cases:
- Mathematical accuracy – While there have been recent releases to improve this limitation, language models are still just that—language models, not mathematical models. Their accuracy in any logical or mathematical task remains suboptimal.
- Accuracy of content – One of the limitations of models like GPT-3 is that despite the large dataset it’s trained on, its knowledge is still limited. GPT-3 was trained in early 2022, so it does not have the most up-to-date information. This can lead to getting information that is simply inaccurate—a dangerous risk if you’re in any Your Money Your Life (YMYL) industries, such as health & medicine, insurance, financial planning, etc.
- Asking for attribution – Asking these models to cite their references could lead to some imaginative and inaccurate responses. Some references might not be real, or the references may not actually contain any arguments to support the claims made by the model.
- Niche industries – Using LLMs for SEO tasks in a particularly niche field or a field that’s frequently changing (e.g., B2B technology, crypto, blockchain, VR, politics, etc.) could lead to subpar results that will only cause more problems.
- On-Brand Cut-and-Paste Content – As mentioned in ChatGPT–Friend or Foe, any AI-generated content needs to be fact-checked and adjusted for your brand and for potential bias. Never copy and paste a large swath of text that has been AI-generated.
- Info on recent events – Models that were pre-trained with older datasets may not always generate up-to-date content.
GPT-4
GPT4 was unveiled on March 15, 2023. It is expected to generate more factual responses and fewer responses prone to “hallucinations” than GPT3.
One of the exciting features rolled out in this update is its modality: its ability to ingest and process not only text, but information from photos. One of the features showcased during the GPT-4 Developer Livestream is the ability to scan a mockup of a website and have GPT4 code a functional website. This isn’t live as of this writing, but this and other features are expected to roll out within the next few weeks to all users (already available for ChatGPT Plus users).
According to OpenAI, the focus of developing this model was rebuilding their training stack, training the model, and assessing the capabilities as well as risks. The model was tested by partners, including Microsoft (Azure and Bing).
Looking forward
At Intrepid, we continue to monitor and test AI language learning models like ChatGPT, GPT-4, BERT, and LaMDA to determine where they can provide efficiencies and to understand risk factors.
We also keep a close eye on how Google and other search engines treat content generated from these models, and when/if these models should be avoided altogether for SEO purposes. We’ll provide updates in this space as things evolve!
RELATED POSTS

SEO in Difficult Times
Is your company in a downturn? Cutting SEO budget may cost more in the long run than just preserving it. Instead, plan smartly. Use these SEO best practices to know how to cut back carefully.
ChatGPT and AI-Generated Content
AI chatbots like ChatGPT can be extremely useful to marketers, but how do they affect content marketing? Should we use ChatGPT for developing blog posts and other web pages? We look at the nuances of brand identity, advanced CRO strategy,
Sign up for the Intrepid newsletter for the latest digital marketing news, tips, and more
"*" indicates required fields
Request a consultation
"*" indicates required fields
